IHI Begins Demonstrating Platform Leveraging Blockchain Technology to Quantify Carbon Dioxide Emissions Across Ammonia Value Chain
IHI Corporation announced today that it has developed and begun demonstrating the Ammonia Carbon Dioxide Traceability Platform. This new setup records the carbon dioxide reduction footprint of ammonia across its value chain, from production through usage.
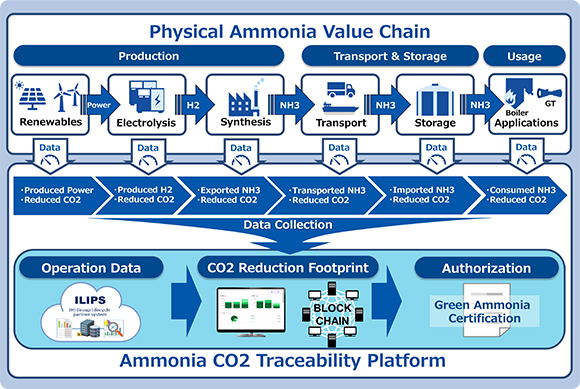
Clean ammonia (see note 1) has attracted considerable attention in recent years as a new fuel source. That is because of its minimal carbon dioxide emissions during production and the absence of such emissions during combustion. To accomplish the adoption of ammonia as a fuel and its expansion, a key factor has been the need to work out a methodology to fully record, manage, and transfer carbon dioxide emissions across multiple players and processes throughout the value chain. This extends from generating and transporting through storing hydrogen and ammonia using electricity from renewable energy sources. Another difficulty has been creating a transparent and reliable technique to calculate carbon dioxide reductions.
The Ammonia Carbon Dioxide Traceability Platform overcomes these challenges by combining ILIPS (for IHI group Lifecycle Partner System) (see note 2), a proprietary Internet of Things platform, with platform technology from Fujitsu Limited. This new setup employs highly reliable data-tracking blockchain technology (see note 3) to calculate, record, and visualize carbon dioxide emissions from ammonia. The emissions at each stage are thus traceable. Value chain players and ammonia consumers can thereby present emissions and reductions figures to stakeholders requiring information for decarbonization endeavors.
IHI started demonstrating the effectiveness of its new platform by establishing a value chain covering two sites. One is the Soma IHI Green Energy Center, which has renewable energy power generation and hydrogen production facilities. The other is the IHI Yokohama Works, which houses ammonia synthesis, storage, and gas turbine facilities. IHI’s effort aims to verify computational techniques and enhance platform functionality. IHI looks to cultivate its platform so anyone engaged in the ammonia value chain can take part in it, undertaking demonstrations in consortiums that it sets up with outside parties. IHI will draw on its efforts to help swiftly commercialize carbon neutral fuels, including fuel ammonia, and their adoption across the economies and reduce environmental impacts by providing high-quality infrastructure.
Notes
- Clean ammonia emits minimal carbon dioxide during its manufacture. There are two types. Green ammonia is produced renewable energy. Blue ammonia is made with fossil fuels. Its emissions from manufacturing are captured and stored underground to minimize them. Green ammonia stands to contribute particularly to carbon neutrality in coming years.
- ILIPS is a common platform for IHI Group products that integrates data on equipment and facilities on cloud servers and uses it in the lifecycle business. IHI is employing this platform, which it launched in 2014, with around 1,500 products as a core Internet of Things and information communication and communications technology vehicle for providing post-delivery value to customers.
- A blockchain is a distributed ledger system in which all network participants share the same data. It employs a framework that makes it easy to detect data falsification. Data is transparent, as all participants can verify it. The data structure comprises a series of records, making it very reliable.
