Rocket Systems and Space Exploration
IHI has participated in Japan’s space development effort from the outset. We have applied our cryogenic-pump and turbomachinery and other technologies to develop and manufacture the turbopumps and gas-jet systems crucial to successful rocket launches. Our involvement in Japan’s space program expanded significantly in 2000, when we acquired Nissan Motor’s Aerospace Division, a pioneer in solid-fuel rocket development in Japan. We play an important role in developing and constructing the Exposed Facilities of the KIBO Japanese Experiment Module, which is a part of the International Space Station program. We support experiments in space by supplying experimental systems needed for cooperative international projects.
Rockets
-
H-IIA rocket/H-IIB rocket

H-IIA rocket/H-IIB rocket,IHI group is developing and producing the turbopumps, solid rocket boosters(SRB-A), 2-stage gas-jet, and the pyrotechnic materials.
- © JAXA
-
M-V rocket

The M-V rocket is one of the world's largest 3-stage solid fuel rocket with a diameter of 2.51 m and it is capable of launching a satellite weighing approximately 1.8 tons into a low-altitude orbit. The M-V rocket has been used to launch satellites developed for space exploration (1997-2006).
- © JAXA
-
Epsilon launch vehicle

The Epsilon launch vehicle is a new rocket, based on the M-V launch vehicle, being developed to provide a more reliable, and responsive space launch system with a lower life-cycle cost for various small satellites customers.
The first flight is scheduled in FY2013.
- © JAXA
-
Development of LNG propulsion system

LNG propulsion system , which uses LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) as a fuel, has advantages of better storability in space and higher density than Hydrogen. By taking these merits, LNG propulsion system can be applied for future project of orbit transfer vehicle and planetary probe mission.
- © JAXA
Rocket Propulsion Systems
-
Liquid oxygen
turbopump for the H-IIA
rocket / LE-7A engine
This pump supplies the liquid oxygen needed to burn the hydrogen fuel in the rocket engines. Together with the liquid hydrogen turbopump, it forms the heart of the rocket.
-
Liquid hydrogen
turbopump for the H-IIA
rocket / LE-7A engine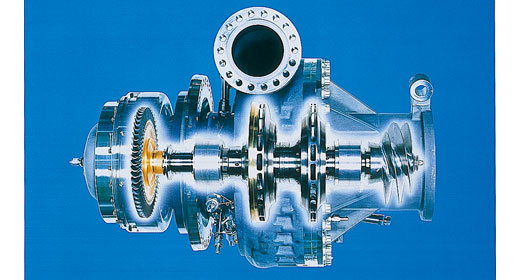
This pump supplies the liquid hydrogen fueling the rocket engines. This forms the heart of the rocket. IHI provides the turbopumps for both the first-stage LE-7A engine and the second-stage LE-5B engine.
Satellite Propulsion Systems
-
Development of
bipropellant liquid
apogee engine, etc.,
used to obtain
geostationary orbit
The apogee engine with 500 N class thrust developed by IHI group has the highest level of performance in the world, rated as top by the clients all over the world along with the 22N thruster.
Space Station-related Equipment
-
International Space Station

The experimental module “KIBO” of the International Space Station that has completed in 2009, is the first manned facility that Japan was in charge of development. The IHI group developed the extravehicular experimental platform as well as the extravehicular pallet for “KIBO”, and also developed the experiment racks and experimental devices installed in inboard labs.
- ©JAXA
-
Development of a propulsion system and exposed pallet for HTV (H-II Transfer Vehicle).

HTV is a space vehicle which transports supplies and collects waste to/from space stations. The IHI Group develops various satellite propulsion systems, including the HTV propulsion system. Since HTV-1 was launched in 2009, it has been fulfilling its mission, earning a reputation of high reliability and satisfying stringent safety requirements.
- ©JAXA/NASA
Ground Test Facilities
-
Ground test facility

In addition to the LNG engine firing test facilities, we also possess test facilities for the satellite propulsion systems and control systems.
Sample Containers, etc.
-
HAYABUSA sample container

Asteroid exploration “HAYABUSA” was launched in 2003 on the M-V rocket No. 5, and the capsule was retrieved from the Woomera Prohibited Area in Australia in 2010. IHI group has the development and manufacturing technologies of the heat resisting materials (CFRP) that can withstand the relentless aerodynamic heating during the atmosphere entry. These materials will be used with the planetary exploration capsules to be produced in future.
- © JAXA
-
Re-entry observation system “i-Ball”

i-Ball is a re-entry data collection device developed by the IHI Group. It is installed on spacecraft, such as HTV, which burn up upon re-entry into the atmosphere. In addition to capturing the nature of destruction upon re-entry, i-Ball measures temperature, acceleration, position and so on using its various sensors. The i-Ball installed on the H-II B-3, launched in September of 2012, has successfully captured images and measured various re-entry data.
-
Next-generation Unmanned Space Experiment Recovery System (USERS)

USERS is a next-generation unmanned space experiment recovery system which was launched by USEF (currently Japan Space Systems or “JSS”) on the H-IIA-3. The IHI Group designed and developed the re-entry module (REM) and Super Conductor Gradient Heating Furnace (SGHF) as well as oversaw re-entry operations and searched recovery work. In May of 2003, the module was successfully recovered in the Pacific Ocean, east of Ogasawara, making it the first time a spacecraft was recovered from orbit by Japan.
- ©JSS
Inquiries about products
