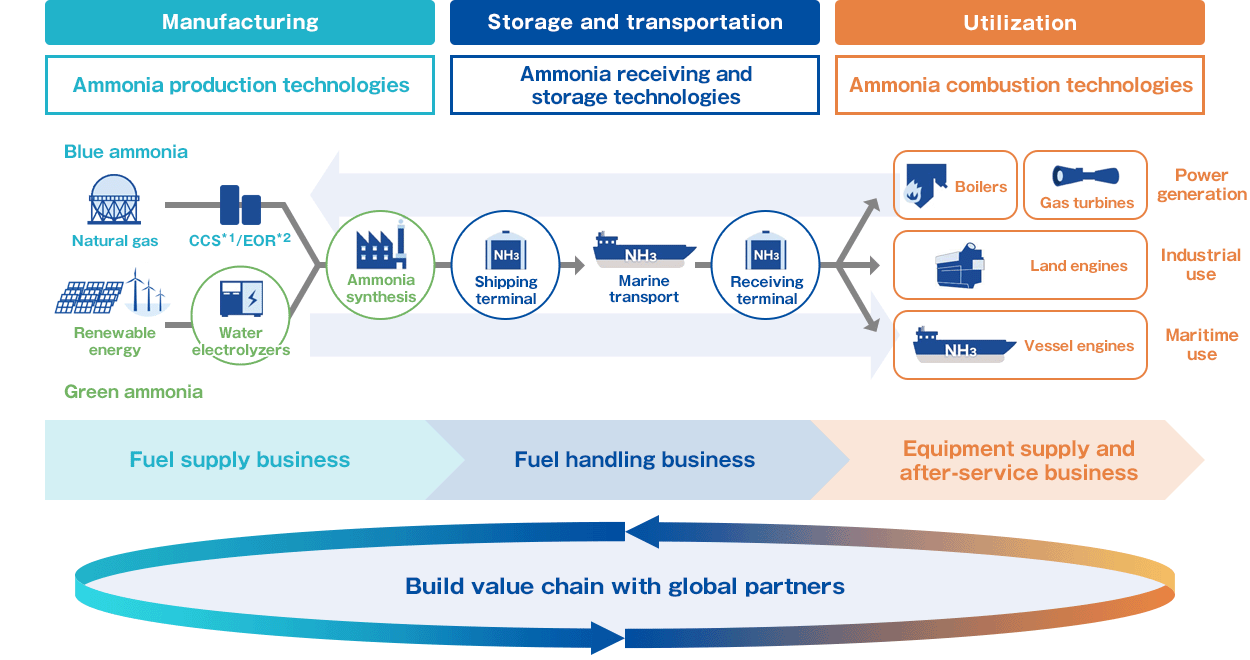
Generating Energy by Using Ammonia for Fuel
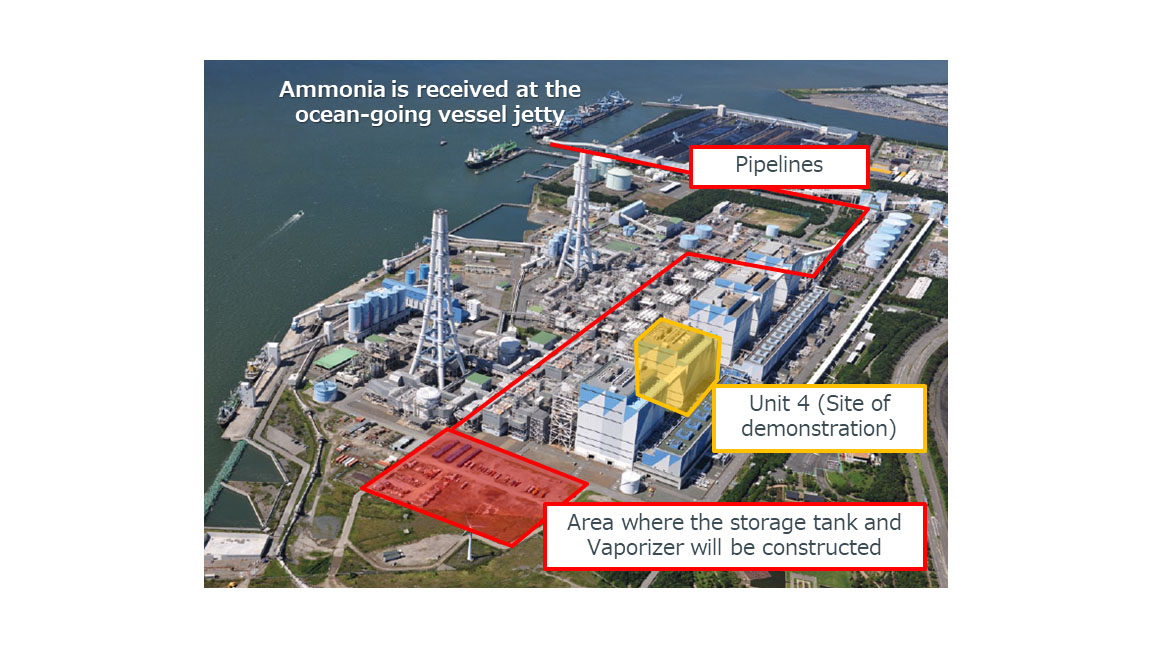
Demonstrating the world’s first large-scale commercial coal-fired power generator using 20% ammonia fuel
Since June 2021, IHI has been working in tandem with JERA Co., Inc. to demonstrate “Development of Technologies for Carbon Recycling and Next-Generation Thermal Power Generation/Research, Development, and Demonstration of Technologies for Ammonia Co-Firing Thermal Power Generation,” a project subsidized by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). Under this project, the world’s first demonstration testing of large-volume fuel ammonia substitution for a large-scale commercial coal-fired power generator was conducted at Hekinan Thermal Power Station Unit 4 from April 1, 2024. On April 10, a 20% substitution of fuel ammonia for operation of rated output of one million kW has been achieved successfully.
IHI will apply the knowledges gained through the demonstration test to establish a combustion technology that increases the ammonia ratio to more than 50% at thermal power plants and develop burners for 100% ammonia combustion.
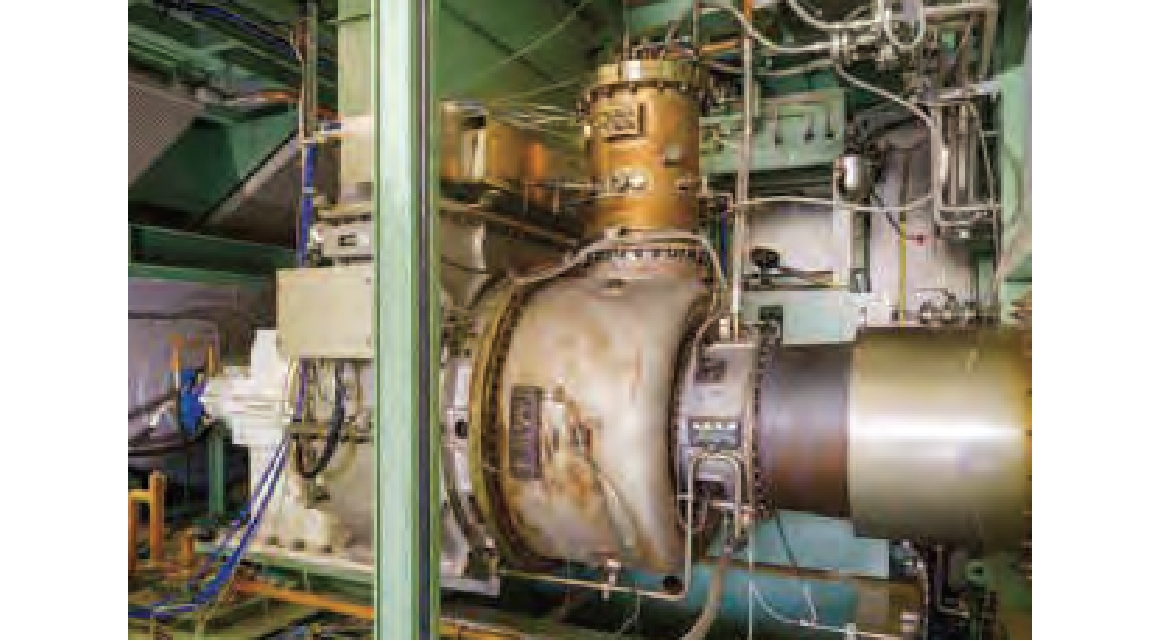
Toward the commercialization of gas turbines using 100% ammonia
As commissioned by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), IHI has been working to develop the technology for a 2,000 kW-class gas turbine that achieves combustion with natural gas by directly spraying liquid ammonia into the combustion chamber. In June 2022, we succeeded in achieving the world’s first 100% combustion of liquid ammonia, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by over 99% during combustion.
IHI aims to commercialize ammonia-dedicated gas turbines by 2026.