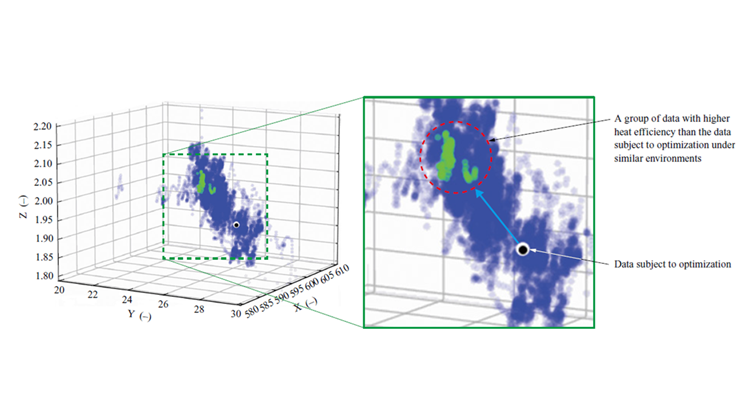
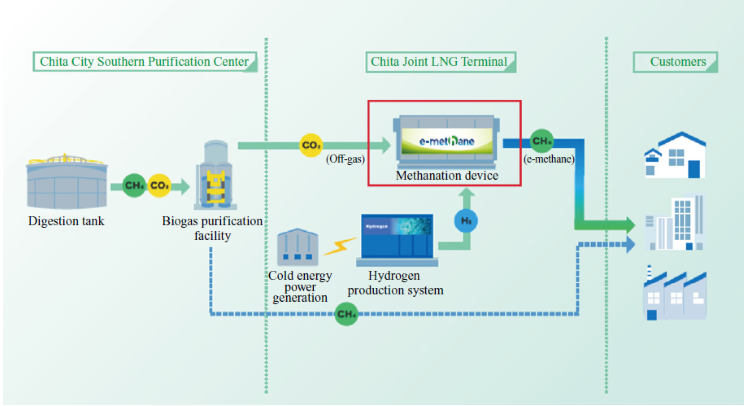
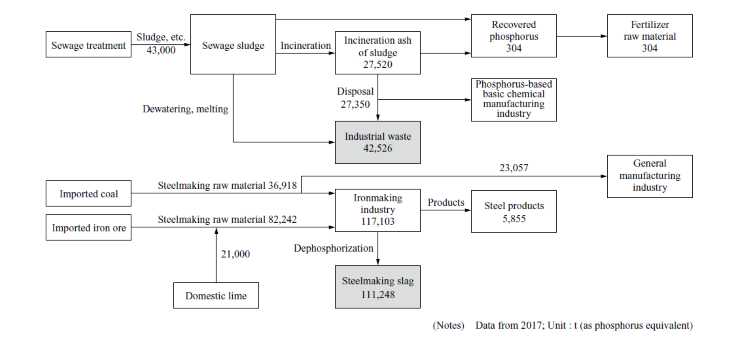
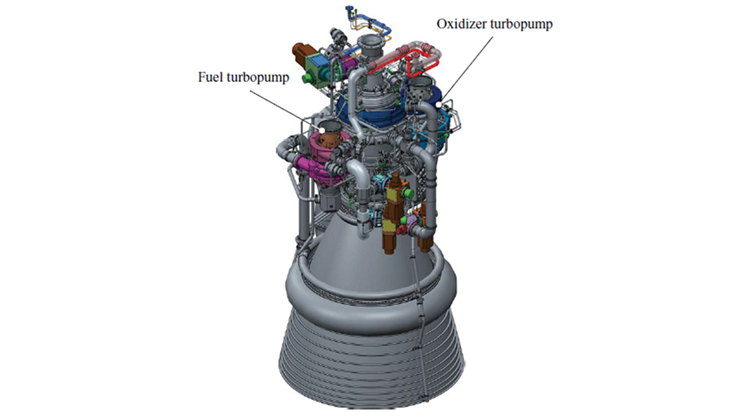
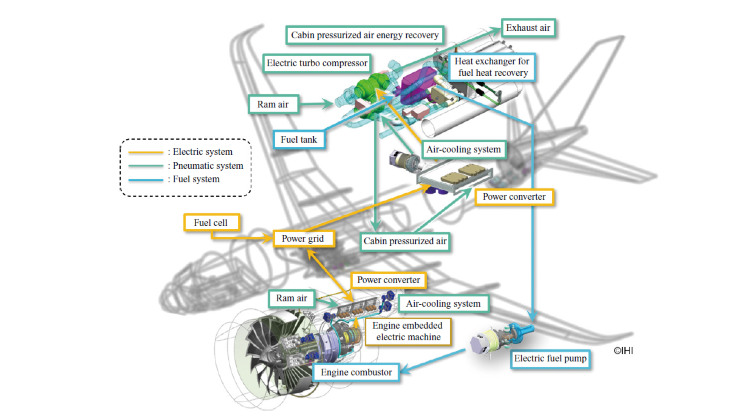
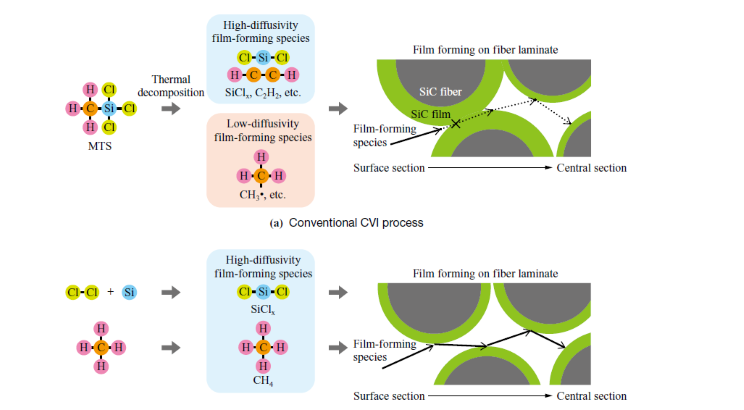
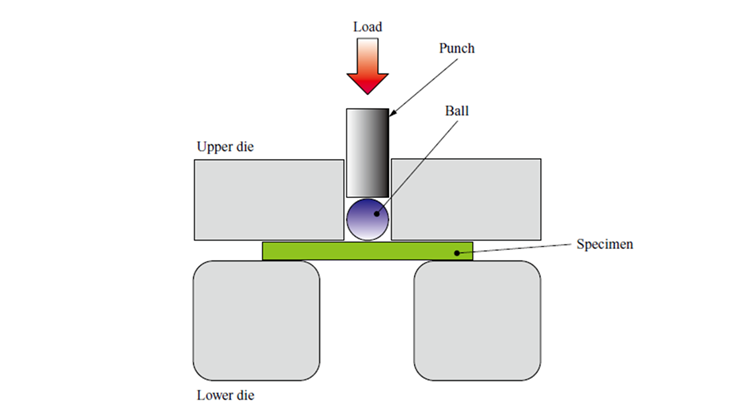
Reduce CO₂ Emissions with -160°C LNG Cold Energy
Delivery of world's largest scale LNG cold power generation unit
- IHI Plant Services Corporation
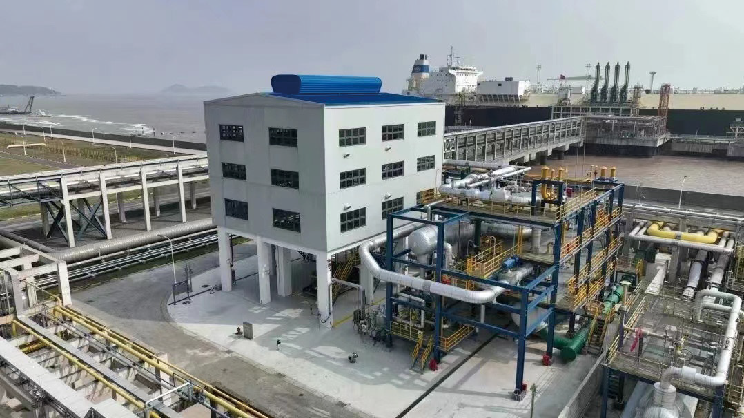
IHI Plant Services Corporation (IPC) delivered an LNG cold power generation unit to Shanghai LNG Company Ltd. in China. This unit is the first of its kind in China. Its introduction has made it possible to reduce CO₂ emissions by up to 10,000 t per year. This article presents an overview of the cold power generation project, including the specifications of the delivered unit, the knowledge obtained through the project, and the unit's operational track record.