Efforts to Develop Environmental Prediction Technologies for Carbon Neutrality
— Recycling carbon dioxide and IoT data —
- Professor at the Advanced Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University
- Ando Hiroyasu
Change
Location
Currently Using The English Site.
Regional HQ’s Websites
Other
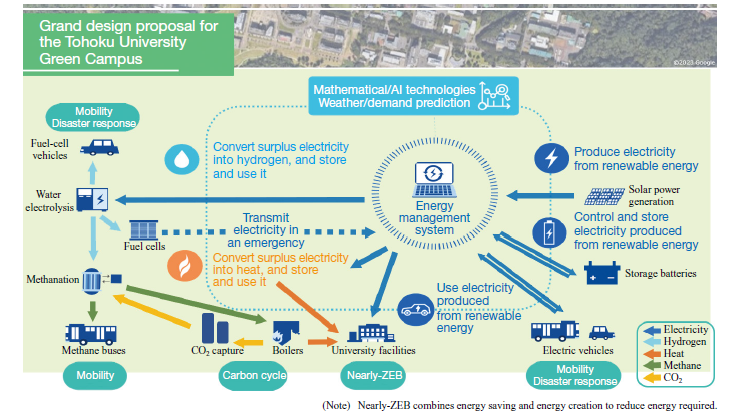
1.Realization of CO2-free and recycling-oriented society
Intermission
Structures That Became Part of Historical Landscapes
2.Technological Innovation
Research and Development that Provides More New Choices for Society
Development of Life Prediction Model for Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMC) with Cooling Holes
Ultimate Limit State Evaluation for Overspeed Burst of Ti-6Al-4V Disk


Efforts to Develop Environmental Prediction Technologies for Carbon Neutrality
— Recycling carbon dioxide and IoT data —
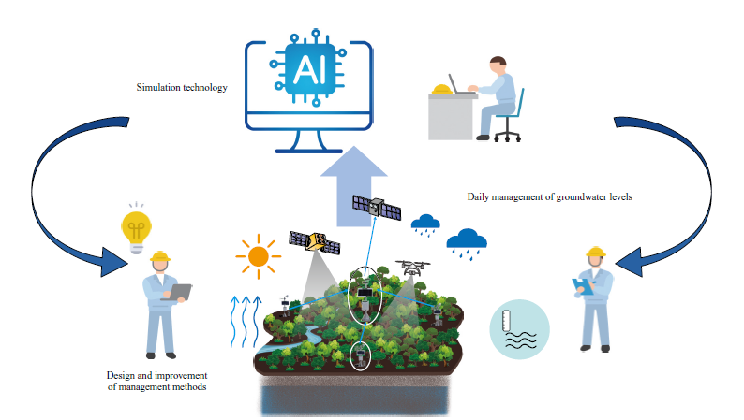
Preserving and Managing Tropical Peatlands Using Simulation Technology
Simulation technology to visualize groundwater levels in tropical peatlands
Forestation businesses that operate in Indonesia's tropical peatlands always need to keep the groundwater levels constant in order to cultivate forests and reduce carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions. For the purpose of managing groundwater levels, we are developing technologies that estimate the levels based on measurement and observation data from tropical peatlands and operational simulations of water management, and aiming at contributing to society through such development.
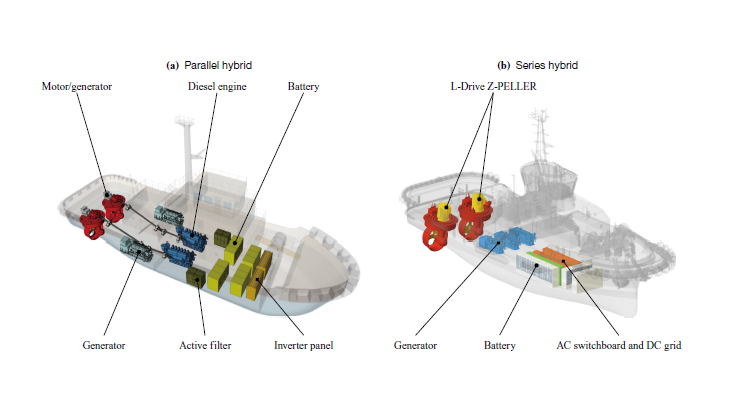
First Environmentally Friendly Next-Generation Electric Propulsion Ship System in Japan
System integration enabling to reduce CO2 emissions by 30%
IHI Power Systems Co., Ltd. has succeeded in significantly reducing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions compared with conventional ships by adopting the DC (direct current) voltage grid system for the series hybrid. The series hybrid uses electric motors for propulsion and a combination of batteries and generators for electricity.

Structures That Became Part of Historical Landscapes

Research and Development that Provides More New Choices for Society
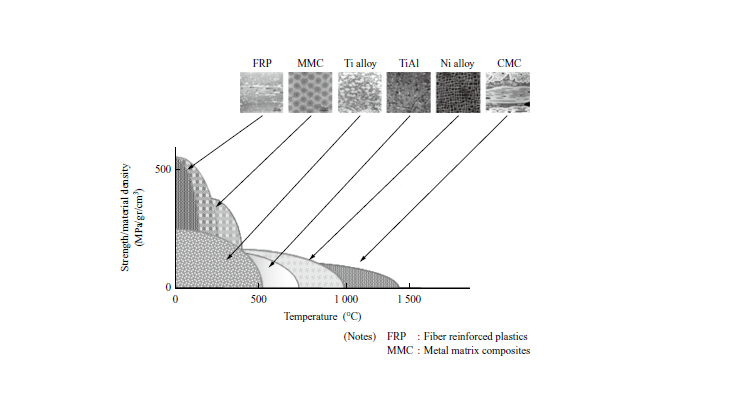
Development of Life Prediction Model for Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMC) with Cooling Holes
Ceramic matrix composites (CMC) have higher heat resistance and specific modulus than Ni-based alloys, thus they are desired to be more applied to aircraft engine parts such as turbine parts. As engine parts are exposed in the condition over the heat durability, multiple holes are generally made on them in order to cool their surface. However, there are few research results on small hole effect for CMC fatigue life. This study focused on this phenomenon. Fatigue tests were conducted using flat plates manufactured with a single hole and multiple holes. As a result of tests, different fracture and crack propagation modes were observed between single-holed and multiple-holed types. A life prediction model was considered to explain the life degradation. The strength parameters were calculated by averaging stress fields, which were predicted by finite element analysis (FEA), in area of CMC unit cell. By using the life prediction model developed in this study, fatigue lives of all types of test pieces with hole can be predicted based on the S-N curve obtained from a smooth-shaped test piece without hole.
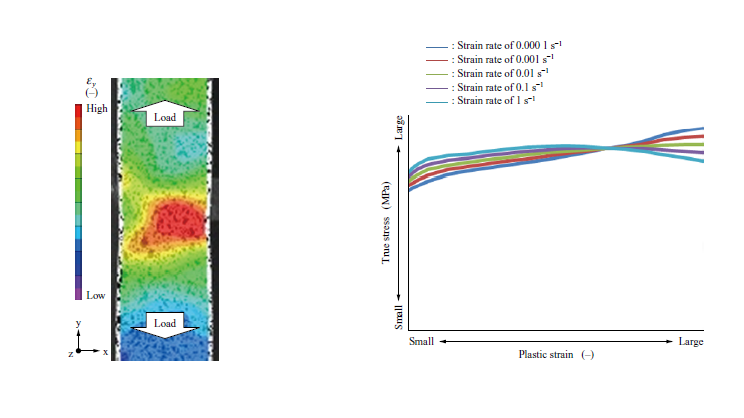
Ultimate Limit State Evaluation for Overspeed Burst of Ti-6Al-4V Disk
In aero engines, it is expected to improve the prediction accuracy of the disk burst rotation speed under overspeed condition and reduce the weight of the disk. In order to improve the prediction accuracy of disk burst by structural analysis, it is important to model the ultimate behavior of the material until fracture. In this study, the ultimate limit state evaluation leading to overspeed burst was carried out by structural analysis for a Ti-6Al-4V disk. The stress-strain relationship up to the high-strain region obtained by the digital image correlation method and the ductile fracture criterion based on the fracture strain dependent on stress state were used in this evaluation.
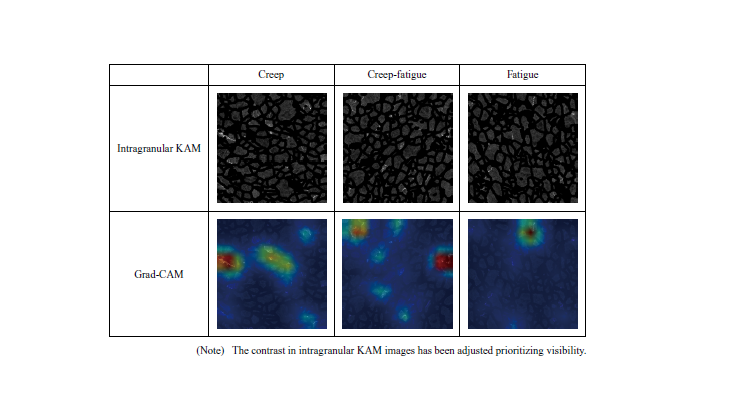
Estimation of Metal Damage Pattern Using Machine Learning
Structural materials undergo various types of damage during use, which can lead to deterioration and failure. To prevent failure or recurrence, it is necessary to identify the causes of damage. However, in conventional damage investigations, estimations have been mostly based on the knowledge and experience of evaluators, leading to subjective and unstable results. It is expected to make generalized estimations, that are not dependent on knowledge or experience, by using machine learning image classification methods for microstructure images of damaged materials. This paper presents the prediction results of machine learning model, which accuracy was 89 % by using EBSD (Electron Backscatter Diffraction) images of three types of damaged materials (creep, creep-fatigue, fatigue). This result shows the potential for accurately estimating damage patterns through this method.